Anti-Static
Static electricity can affect product yields by damaging products when discharged or collecting particles when accumulated, so solutions are required for flex cables. Gore's engineered ePTFE jacket with Anti-Static technology provides a solution for preventing the charging of static electricity in flexing clean cable systems.
Reasons to have the solution
for anti-static is required
for clean cables.
Sensitive electronic components such as semiconductors can be damaged by static electricity, so the solution to prevent static electricity are essential, especially in moving parts during the manufacturing process.
Static electricity can damage circuits when discharged, and if it accumulates beyond a certain limit, it can capture particles of the opposite polarity, so appropriate solutions are required in processes where particulation management is essential.
PTFE is the most negatively charged among the triboelectric series as shown in the table on the right, making it a material that easily generates static electricity.
Gore has developed a cable jacket that minimizes static electricity accumulation (charging) by specially engineered ePTFE material, and is applying it to GORE® Trackless Cable products.

Surface resistance
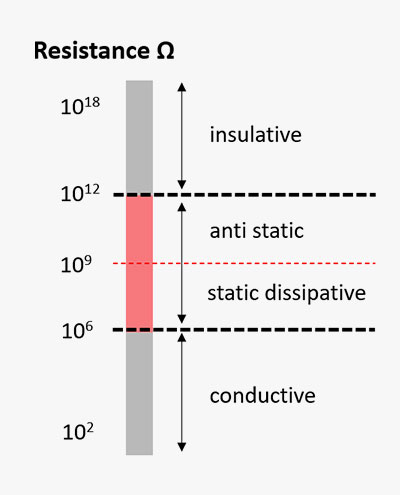
The insulation or outer jacket of the cable uses a non-conductive material for insulation, and in order to prevent static electricity, the non-conductive material must be made in the range of semi-conductive material so that it is still an insulator but static electricity can be dissipated. So, the targetted Static electricity dissipation range for anti-static electricity is 106 to 109Ω.
However, methods such as mixing or coating conductive materials such as conductive carbon are excluded as they can affect the semiconductor manufacturing yield when scattered as particles.GORE® Anti-Static High Flex Cables is the first clean cable system to apply anti-static measures while satisfying all existing performances and maintaining a surface resistance of 109Ω or less throughout the expected life of the product.
Volatages build up
(100V or less)


GORE® Anti-Static High Flex Cables was developed so that the voltage generated by friction does not exceed 100V. (Based on 23℃, 45% Rh)
The graph above shows the values compared by measuring the voltage while frictioning the existing material and the Anti-Static material up to 1000 times.
Additional tests
In order to verify whether surface resistance or voltage build up after friction maintains the same performance even when the cable is actually flexing, measurements were made while flexing the actual cable for up to 10 million cycles, which is the expected flex life of the product.
The cable might be flexing under cleanroom conditions (23℃, 45% Rh), but it is exposed to various environmental conditions before being installed to the equipment after manufacturing and during the process of being installed in the equipment and transported to the cleanroom of the final customer. In order to ensure that there is no change in the physical properties under these conditions, Gore conducted tests under various environmental conditions during the product development period.
In order to compare the particulation performance with existing products, we commissioned a particulation test to an external research institute (Fraunhofer IPA) and confirmed that it satisfied ISO Class 1 up to 1 million cycles of flexing. We also tested the product ourselves to verify that it has the same level of particulation performance up to the expected life time of 10 million cycles and verified that it is at the same level as existing products.
With only a simple anti-static coating, the anti-static function may deteriorate or there might be particulation depending on the various conditions mentioned above, which may significantly change the performance of the product.
